Our immune systems are comprised of dozens of different types of cells, antibodies, cascades, and more. This is often why immunology is such a daunting subject for so many students.
One key component for making sense of the world of immunology is understanding the difference between innate and adaptive immunity.
Both are incredibly important for fighting off infection and work differently yet synergistically to provide a broad defense.
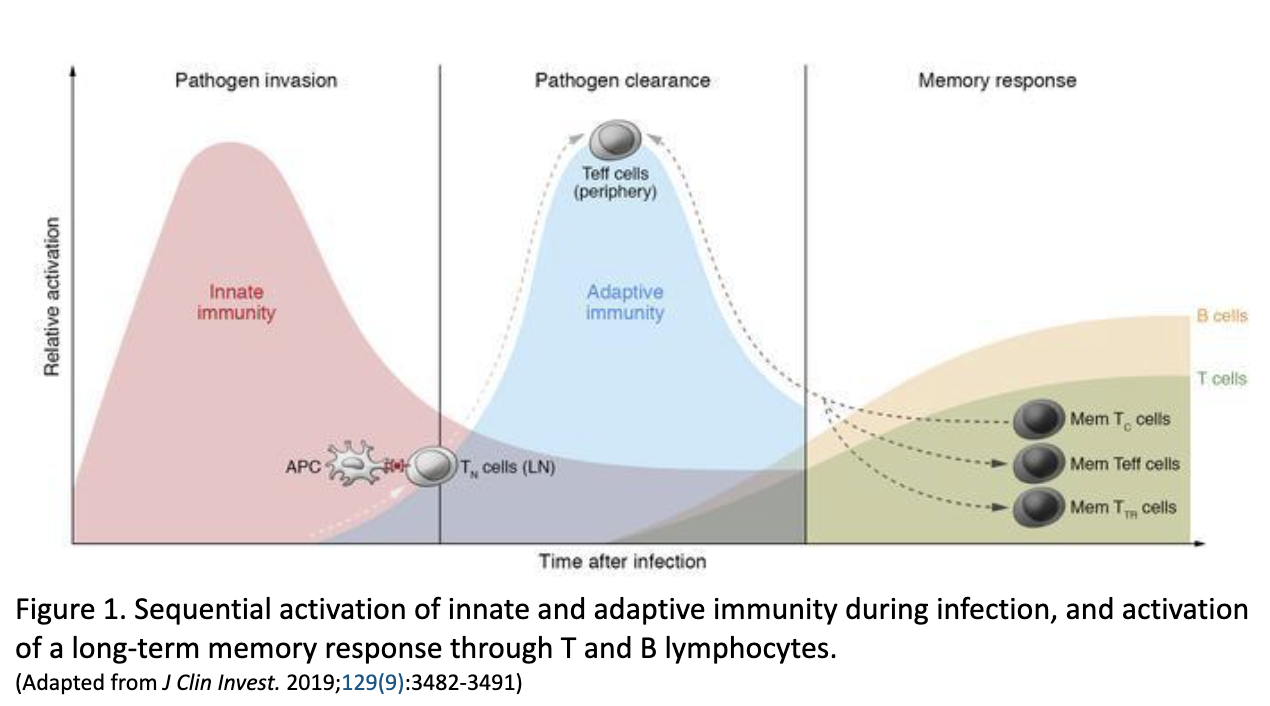
When we talk about the difference between innate and adaptive immunity, it is helpful to differentiate the two based on infection timeline (Figure 1). Innate immunity is the initial defense we have against infection and is what the initial rapid immune response relies on. Meanwhile, adaptive immunity is activated later since it requires exposure to the pathogen before it can work against it. When we think of “building immunity” against something, we are referring to the memory properties of adaptive immunity. Adaptive immunity is also specific to whatever pathogen it has “learned” to fight whereas innate immunity is non-specific.
Now let’s explore each type a little closer...
Innate Immunity
- Non-specific
- Starts working as soon as we are exposed to a pathogen.
- Much older evolutionarily and highly conserved across species
- Fun fact: Some organisms that are more “prehistoric” or simple only have innate immunity. One example of this is the American Lobster!
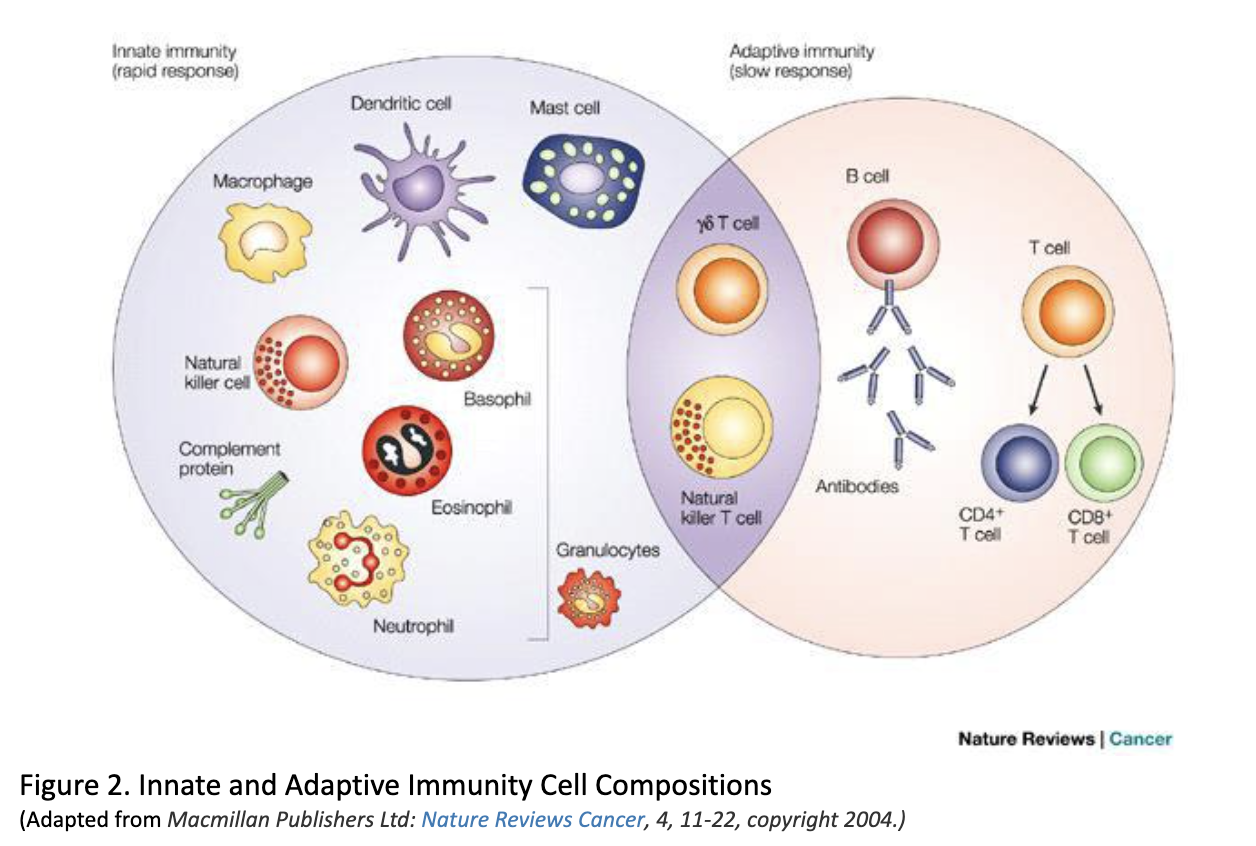
- Comprised of phagocytic cells, epithelial and endothelial cells, natural killer cells, innate lymphoid cells, and platelets (Figure 2).
- Phagocytic cells = granulocytes (i.e., neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, and mast cells), monocytes/macrophages, and dendritic cells.
- Mechanistically 🡪 Use cytokines or direct cell-cell interactions (ex. Phagocytosis).
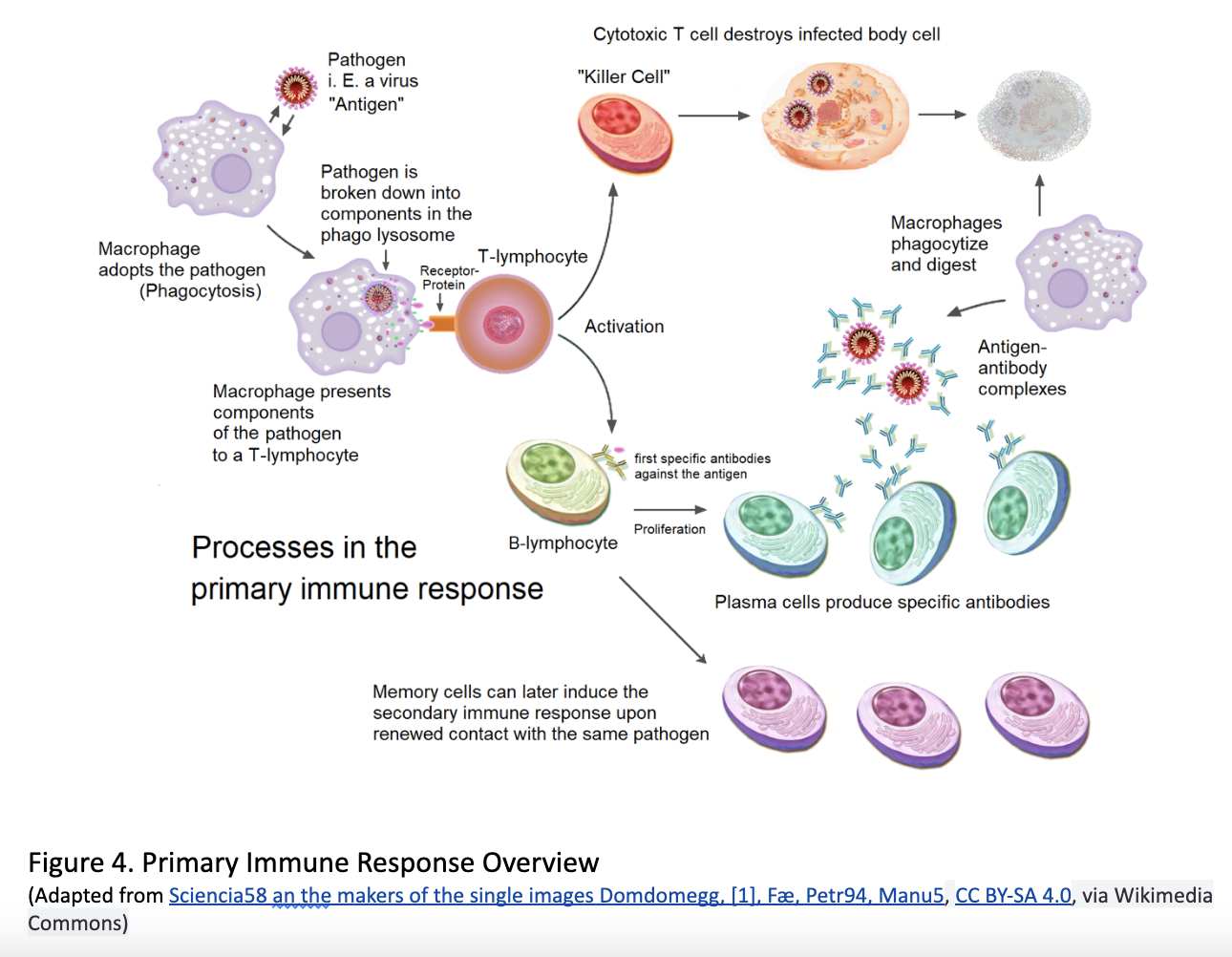
- Work to activate adaptive immune system by presenting antigens from the pathogen for T-cells and B-cells to “learn.” (Figure 4)
Adaptive immunity
- Specific to pathogen/antigen
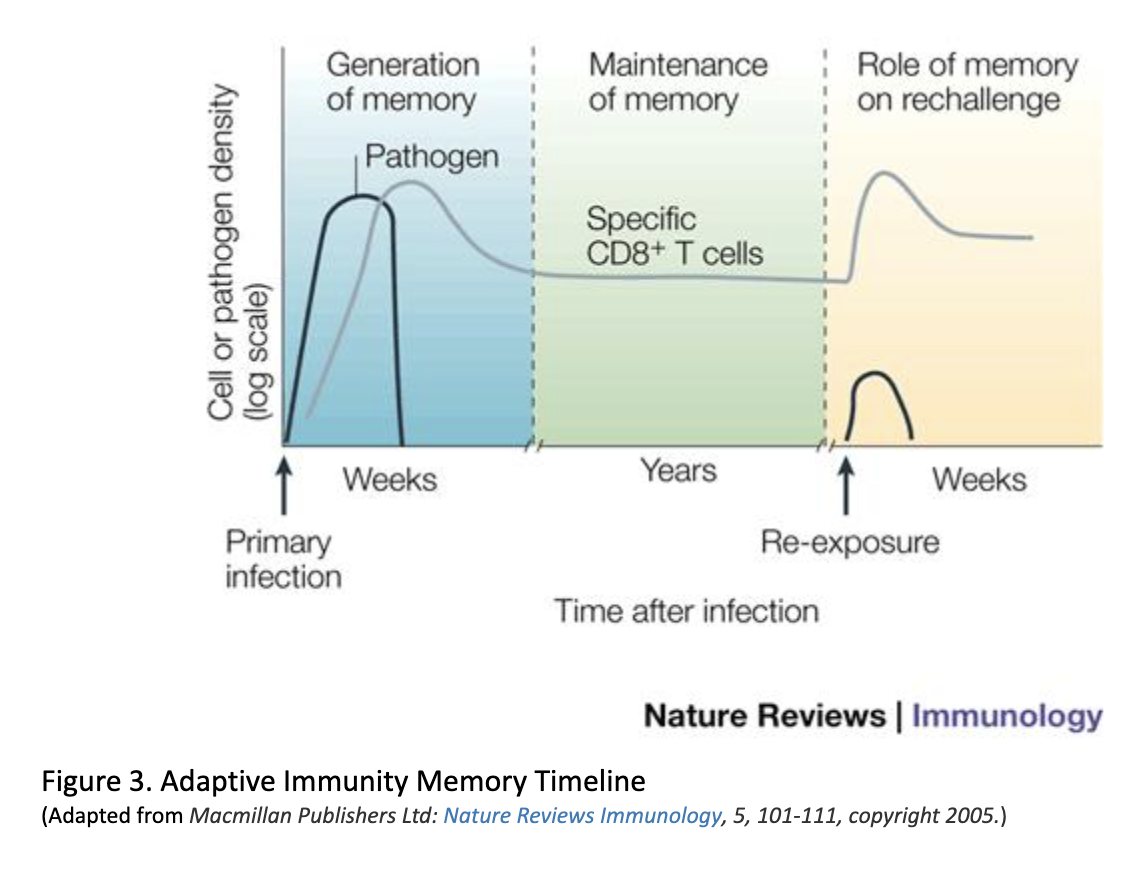
- Needs more time after exposure to build “memory” to begin fighting off infection (Figures 1 & 3).
- Comprised of B-cells and T-cells--lymphocytes (Figure 2)
- T-cells (Two Main Types + One Regulatory)
- Helper T-cells (CD4+)
- Help signal/activate other immune cells.
- Cytotoxic T-cells (CD8+)
- Kill infected cells and tumor cells.
- Regulatory T-cells (CD4+ CD25+)
- Smaller sub-population of T-cells that work to suppress immune cells when necessary to prevent attacking healthy host cells.
- Helper T-cells (CD4+)
- B-cells
- Responsible for antibody creation and secretion
- T-cells (Two Main Types + One Regulatory)
Below is a simplified general overview that shows how the innate and adaptive immune system interact and work together to fight off infection.
Conclusion
We have now covered a brief overview of innate and adaptive immunity. In short, we can think of innate immunity as a non-specific, rapid immune response comprised of several cell types (ex. Granulocytes and Macrophages) and adaptive immunity as a specific, long-term memory based immune response comprised of T-cells and B-cells.
However, is this division this clear-cut in reality? What about the cells that fall in-between as seen in Figure 2? It turns out that these two categories are not as perfectly divided as we initially thought. One example is NKT cells. Without diving in too deeply, these cells share properties of both NK cells and T cells. There has also been research that suggests memory properties in NK cells. While the simple distinctions between innate and adaptive immunity is important to understand for your classes and exams, it has been discovered to be much more complicated as we continue to research it more - which makes it a fascinating field to follow!


Comments