To solve many of the quantitative questions on the GMAT, it is essential to understand a couple key equations. This article will clearly lay out 3 very important formulas.
1. Pythagorean Theorem: a2 + b2 + = c2
The Pythagorean Theorem only applies to right triangles, which is a triangle that has one angle measured 90 degrees. In this equation, a and b represent the two legs of the triangle (shorter sides) and c represents the hypotenuse (longer side opposite the right angle). This theorem helps solve many different GMAT Quantitative geometry questions. For example, you might be given that it is a right triangle and the lengths of two of the sides, and you will be then asked to find the length of the 3rd side by plugging into the above equation.
Be sure to also review common Pythagorean triples such as 3: 4: 5 and 5: 12: 13 and 6: 8: 10, in addition to 45-45-90 and 30-60-90 triangles.
2. Average, Sums, and Weighted Average
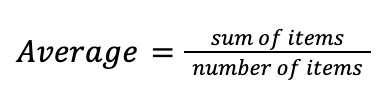 The average is the sum of all the numbers in a list divided by the number of items in the list. This average formula can be rearranged to isolate the “sum” of the items. By multiplying both sides by “number of items,” you would then have the formula, sum of items = average * number of items. The GMAT expects students to leverage this formula for many different problems.
The average is the sum of all the numbers in a list divided by the number of items in the list. This average formula can be rearranged to isolate the “sum” of the items. By multiplying both sides by “number of items,” you would then have the formula, sum of items = average * number of items. The GMAT expects students to leverage this formula for many different problems.
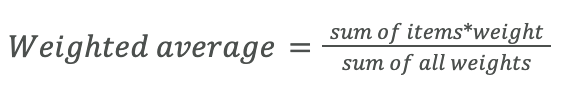 The weighted average is similar to typical average questions; however, the difference is that not all values in the set contribute uniformly to the mean. For the purposes of the GMAT, this topic could come up in a problem where we are asked to combine groups with different sizes and group averages. In problems such as this, the goal would be to find the average of all groups together. Keep in mind that although this is the primary equation to solve the weighted average, you can also solve weighted average problems through leveraging 1) proportions / percentages of each group and 2) proportional placement of total averages.
The weighted average is similar to typical average questions; however, the difference is that not all values in the set contribute uniformly to the mean. For the purposes of the GMAT, this topic could come up in a problem where we are asked to combine groups with different sizes and group averages. In problems such as this, the goal would be to find the average of all groups together. Keep in mind that although this is the primary equation to solve the weighted average, you can also solve weighted average problems through leveraging 1) proportions / percentages of each group and 2) proportional placement of total averages.
3. Distance equation: Distance = speed * time
Distance refers to how far apart things are (e.g., points, people, places), speed refers to the rate of travel, and time refers to how long it takes to travel. Distance problems are very common on the GMAT, and they make up a majority of the quantitative section (almost 60%!). Beyond this simple distance equation, another important topic is average speed.
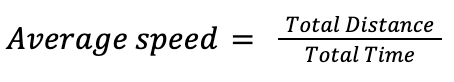 Average speed, as seen above, is the total distance traveled over the total time spent traveling. Even if you have multiple parts of one trip, you will have to add up the distances of each part and then divide it by the total time of each part. In a sense, average speed captures the constant speed needed to travel the total distance in the total time.
Average speed, as seen above, is the total distance traveled over the total time spent traveling. Even if you have multiple parts of one trip, you will have to add up the distances of each part and then divide it by the total time of each part. In a sense, average speed captures the constant speed needed to travel the total distance in the total time.
Comments