Let’s talk about a concept that can be confusing when you’re first studying calculus: limits. When you’re first introduced to limits, you’ll often hear your professor say things like,
“What is the limit of f(x) = 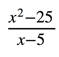 as x approaches 5?”
as x approaches 5?”
When worded like that, limits don’t sound very natural or intuitive – but in today’s post, I’m going to convince you that limits are a very natural way of looking at the world. I’ll also go over some examples of limits that we can solve without doing any “math” at all!
An Example: Riding a Bike
Let’s start with an example. Imagine that you are watching your friend ride her bike along a smooth surface, and that you are drawing a graph of the position of her bike as a function of time.

The graph might look something like this:
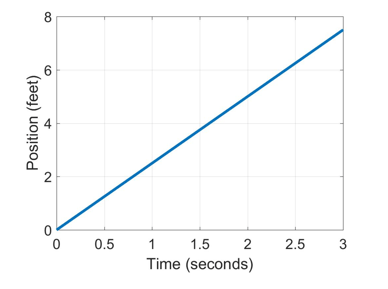
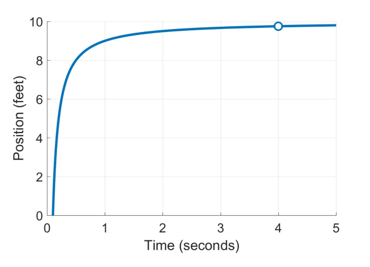
Now, let’s say that as you continue drawing the graph, you momentarily look away from your friend, so you miss where she is at the time 4 seconds. So your graph now has a “hole” in it, at the moment that you looked away. 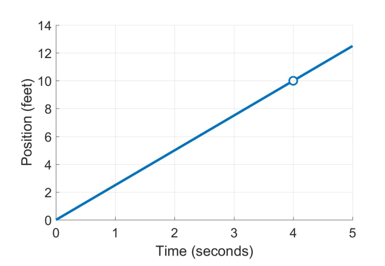
Even though you don’t know for sure where your friend was at 4 seconds, can you guess where she was? Sure you can – she was probably at 10 feet. How do you know? Because right before 4 seconds, she was just less than feet, and right after seconds, she was just past 10 feet. Unless she was magically transported at the exact moment you looked away, she must have gone through 10 feet for the graph to make sense.
Limits are simply this very obvious idea – that you can “guess” what values a function takes at a point, based on what value it takes at neighboring points.
When you see an expression like: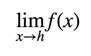
You should think to yourself: hmm, what value would I guess the function f(x) to take when x is about h, based ONLY on values that the function takes CLOSE to h? (The arrow in the expression 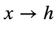 just means “approaches”).
just means “approaches”).
If f(x) is the position of your friend at time x, then
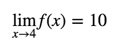
I want to point out that that the function doesn’t have to be linear for you to to be able to take limits. Let’s consider a different example, where your friend is riding her bike again, but now is slowing down, as she reaches a stop sign.
The graph of her position might look something like this (this is definitely not a linear function!):
In this graph, your friend starts out driving very quickly, but rapidly slows down, starting at at around half a second. Again, even though we “looked away” at x=4, and so the function f(x) is undefined at that point, we can still evaluate the limit. In this case,
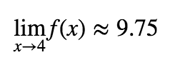
Limit to Infinity
So we’ve seen so far that limits allow us to “guess” the behavior of functions at those points where we don’t know the exact value of the function, for whatever reason.
Often times, we are interested in knowing what value a function will take at infinity. We can’t graph a function all the way to infinity, and neither can we “plug in” infinity into a formula to evaluate the answer directly.
It turns out that this is another case where limits can help us out. Remember, limits are our best “guess” of how a function will behave based on the points we do know. So for example, if we look at that last graph again (reproduced below) – when your friend is approaching a stop sign – we might ask, “if she continues her current trajectory, where will she end up after an infinite amount of time?”
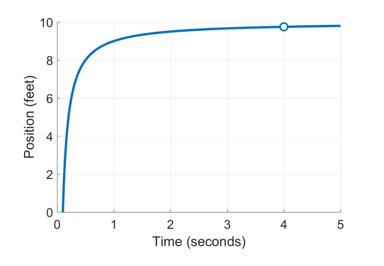
In this case, it might be reasonable to say that there seems to be an asymptote at 10 feet. The idea here is that your friend is slowing down, slowing down, and eventually, she will grind to a stop right at the stop sign, located at about 10 feet. If the function doesn’t change (in other words, she doesn’t start biking again), then her position after an infinite amount of time will be 10 feet.
In mathematical language, we write this as:
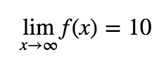
Limits to infinity are a little bit different than limits at a finite point – instead of looking at neighboring values, we instead look at the general trend of a function, f(x), and try to guess where the function will end up as becomes larger and larger.
Sometimes the limit of a function at infinity may be positive or negative infinity! Can you figure out what the limit of the first (topmost) graph is, as 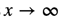 ?
?
When the Limit Doesn’t Exist
There are also cases where the limit doesn’t exist (or you might hear that the limit is undefined). Here’s an example of a case like that:
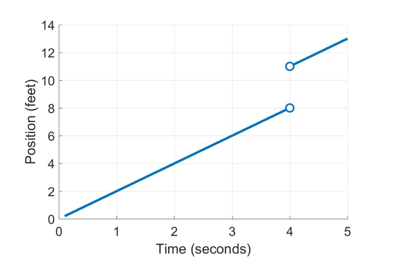
What would you say is the limit when  ? It depends where you look! If you look at times smaller than 4 seconds, it would seem that she would be at 8 feet, but if you look at times greater than 4 seconds, it would seem that she would be at 11 feet! When you have contradictory guesses, you can say that the limit simply doesn’t exist.
? It depends where you look! If you look at times smaller than 4 seconds, it would seem that she would be at 8 feet, but if you look at times greater than 4 seconds, it would seem that she would be at 11 feet! When you have contradictory guesses, you can say that the limit simply doesn’t exist.
Of course, in most real-world situations, this doesn’t happen! For the limit to not exist, you friend must have magically transported from 8 feet to 11 feet at the exact moment you weren’t looking! The power of limits is that they accurately describe most real-world functions, which are continuous and smooth.
Wow, Are Limits That Simple?
Yup, that’s all there is to the concept of a limit. In reality, you usually won’t be given graphs from which to evaluate limits. Instead, you’ll be given mathematical functions, from which you will have to determine what neighboring values are, next to the point that you’re interested in. There will be cases where neighboring values take contradictory values, and the limit isn’t defined. In other cases, you will have to consider whether asymptotes exist in a problem, as you decide what values functions approach at positive or negative infinity.
But hopefully, now that you have a concrete picture in mind, you’ll be able to tackle these problems with confidence!
Abu is one of our incredible mathematics tutors in Cambridge. If you're interested in working with him in Cambridge or online, you should contact us today!
Are you looking for more content on mathematics? Check out some of our previous blog posts below!

Comments