Physics can be a very time-intensive section on the MCAT. There are numerous equations to memorize and parse through for each question and it is not always obvious which are relevant. You can waste a lot of valuable time guess-and-checking equations that have the related variables in them. I will illustrate some techniques from personal experience to save time and find the right answer when approaching one of these passages!
Step 1: Equations as Building Blocks
Firstly, it is critical that you memorize the most relevant physics equations for the test day. Many are not going to be included in the test, but they do expect you to know them. These should encompass the topics of mechanics and energy, fluids and gases, thermodynamics, sound, lights and optics, electrostatics and circuits, and magnetism. It can be helpful to group equations that yield the same variable since the MCAT commonly gives values that require multiple connected equations to be solved. Below are a few associated equations that are important to remember for test day:
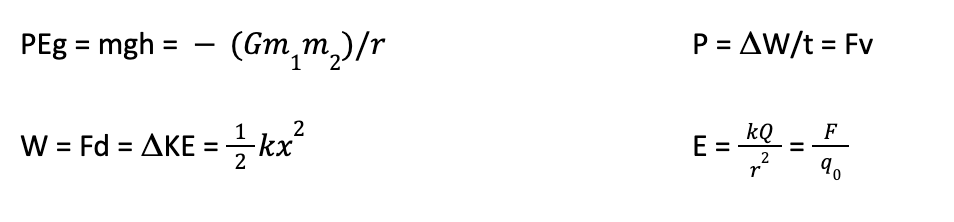
Step 2: Connect Equations with Relevant Concepts
Next, connect each equation to the types of concepts that it will be useful for. This can be accomplished by becoming familiar with topics that the AAMC frequently tests. These include atomic and nuclear phenomena, circuits, movement and forces, and fluid and gases. They do test many topics outside of this list, but these are easily tied to biological systems questions. For example, you could see several physics questions in a passage about blood flow or lung capacity. It is helpful to recognize that they are most likely asking for a pressure equation and to connect relevant topics (Bernoulli’s principle or the Venturi effect).
Another common topic is body kinetics as models of movement and force physics. For these, it is important to recognize the interplay between torque and forces in muscles. Always label your forces and keep track of units. One example would be calculating the force exerted by the biceps muscle to hold the forearm steady when a load is placed on the hand. An important feature to keep in mind for this problem is the elbow angle which impacts the amount of force the bicep muscle needs to exert. Personally, I would approach this problem and draw a simplified drawing of the joint as a flat surface with a rotation point, filling in relevant forces at play and equations that could link them. There are many strategies to employ when solving MCAT physics problems. The most important, however, are to organize your time and keep track of forces and equations involved.
Step 3: When in Doubt, Trace the Units
One final strategy to employ when stuck on a physics problem, is to look at the multiple choice answer units and connect them to equations which will yield those units. This does require you to have intimate knowledge of each equation and the units involved, but this is a great starting point if you are truly lost or to check your work.
Comments