-2.png?width=1080&name=Statistical%20Mediation%20%26%20Moderation%20in%20Psychological%20Research%20(1)-2.png) Balancing redox reactions is an essential skill for the Chemical and Physical Foundations section of the MCAT, the GRE Chemistry Subject Test, and the AP Chemistry Exam. Today, we will learn how to use the half-cell method for balancing redox reactions in acidic and basic solutions. We will first balance a redox reaction in acidic solution, then we will balance the same redox reaction in basic solution.
Balancing redox reactions is an essential skill for the Chemical and Physical Foundations section of the MCAT, the GRE Chemistry Subject Test, and the AP Chemistry Exam. Today, we will learn how to use the half-cell method for balancing redox reactions in acidic and basic solutions. We will first balance a redox reaction in acidic solution, then we will balance the same redox reaction in basic solution.
Balancing Redox Reactions in Acidic Solution
Consider the following unbalanced redox reaction:
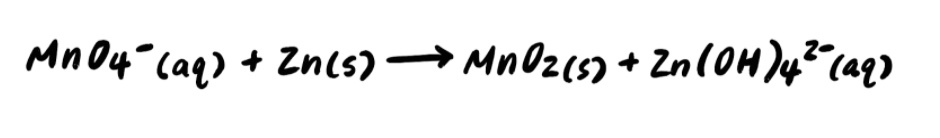
Let’s try to balance this reaction in acidic solution.
Step 1: Divide the reaction into half reactions
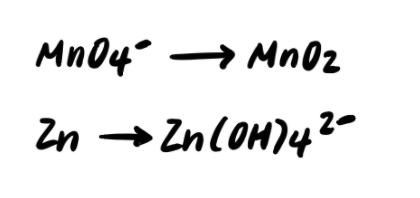
Step 2: Balance the elements other than H and O
Fortunately, all atoms other than H and O are already balanced, so we can move on to the next step.
Step 3: Balance the O atoms by adding H2O
Step 4: Balance the H atoms by adding H+
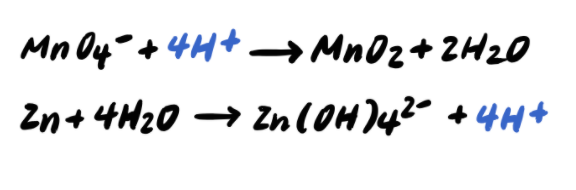
Step 5: Balance the charges by adding e-
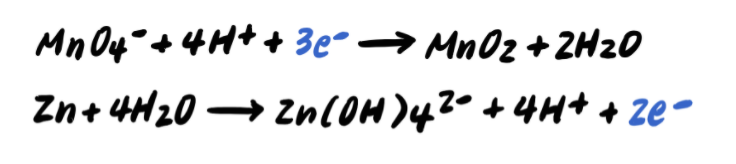
Step 6: Add the half reactions and simplify
Because the number of electrons in the first half reaction (3e-) does not equal the number of electrons in the second half reaction (2e-), we must multiply the reactions by coefficients so that the electrons will cancel out when we add them. In this case, we multiply the first reaction by 2 to yield 6e-, and the second reaction by 3 to yield 6e- as well.
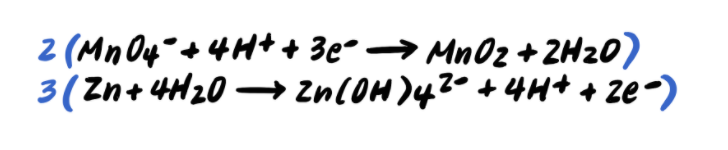
Carrying this out, we get:

Now we can add the two reactions, and we notice that the electrons on both sides cancel out.
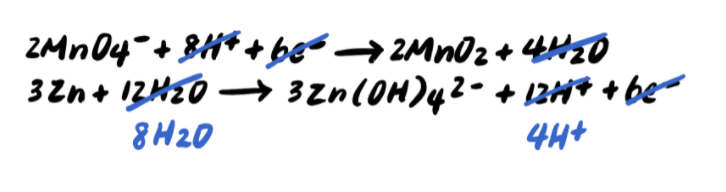
Thus, our balanced reaction is:
To summarize, the steps for balancing redox reactions in acidic solution are as follows:
- Divide the reaction into half reactions
- Balance the elements other than H and O
- Balance the O atoms by adding H2O
- Balance the H atoms by adding H+
- Balance the charges by adding e-
- Add the half reactions and simplify
Now that we have learned how to balance redox reactions in acidic solution, we will learn how to balance the same reaction in basic solution.
Balancing Redox Reactions in Basic Solution
Balancing redox reactions in basic solution is slightly more complicated than balancing in acidic solution because we must add both H+ and OH- to each half reaction. I will highlight the additional steps while we move through the process.
Let’s return to the same unbalanced reaction as above:

We will try to balance this reaction in basic solution.
Step 1: Divide the reaction into half reactions
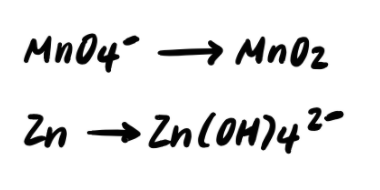
Step 2: Balance the elements other than H and O
Fortunately, all atoms other than H and O are already balanced, so we can move on to the next step.
Step 3: Balance the O atoms by adding H2O
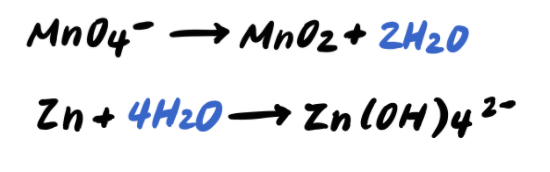
Step 4: Balance the H atoms by adding H+
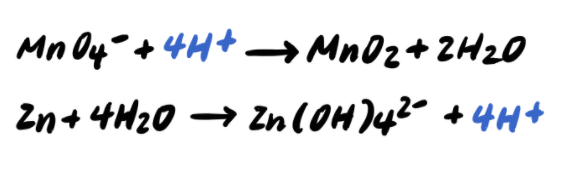
Step 5: Add OH- to BOTH SIDES neutralize any H+ [ADDITIONAL STEP]
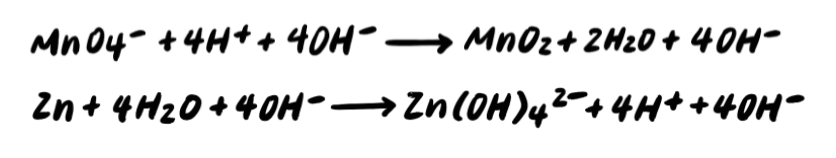
Step 6: Combine H+ and OH- to make H2O [ADDITIONAL STEP]
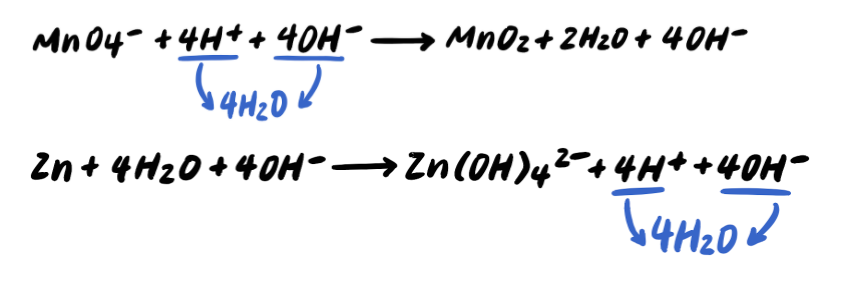
We simplify the equations to get:
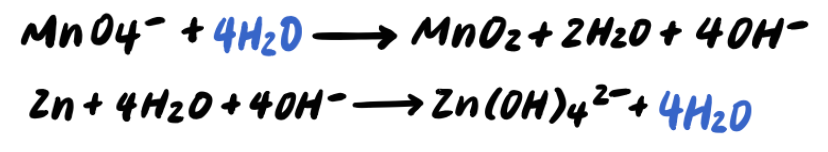
Step 7: Simplify by cancelling out excess H2O [ADDITIONAL STEP]
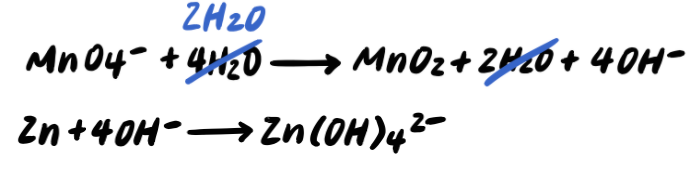
Step 8: Balance the charges by adding e-
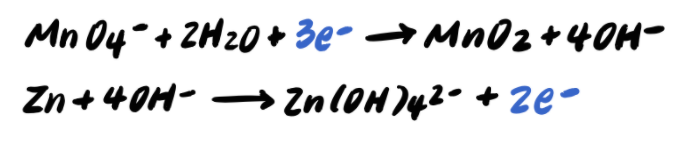
Step 9: Add the half reactions and simplify
Recall that we must multiply the reactions by coefficients so that the electrons will cancel out when we add them. In this case, we multiply the first reaction by 2 to yield 6e-, and the second reaction by 3 to yield 6e- as well.
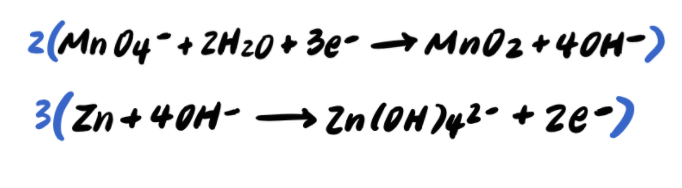
Carrying this out, we get:
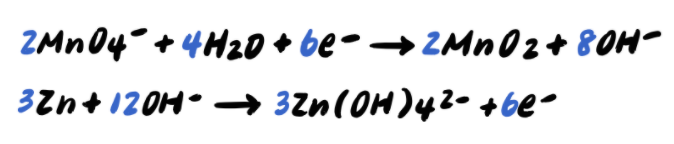
Now we can add the two reactions, and we notice that the electrons on both sides cancel out.
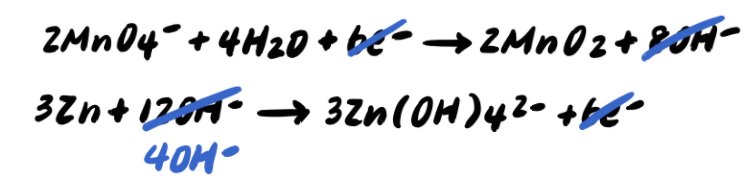
Thus, our final balanced reaction is:
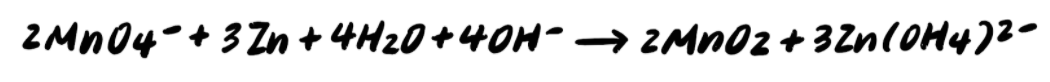
To summarize, the steps to balancing a redox reaction in basic solution are as follows:
- Divide the reaction into half reactions
- Balance the elements other than H and O
- Balance the O atoms by adding H2O
- Balance the H atoms by adding H+
- Add OH- ions to BOTH SIDES neutralize any H+
- Combine H+ and OH- to make H2O
- Simplify by cancelling out excess H2O
- Balance the charges by adding e-
- Add the half reactions and simplify
And there we have it! I hope you enjoyed this guide and found it helpful. For more practice on balancing redox reactions or other general chemistry concepts, I recommend checking out Khan Academy, the UWorld MCAT Question Bank, or the ExamKrackers 1001 Questions in MCAT Chemistry workbook. If you are interested in working with me to prepare for the MCAT, please reach out via the contact button below!
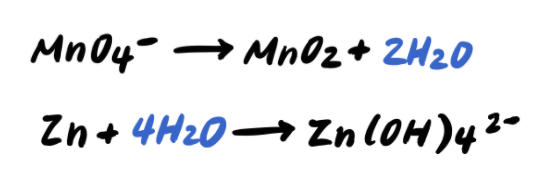
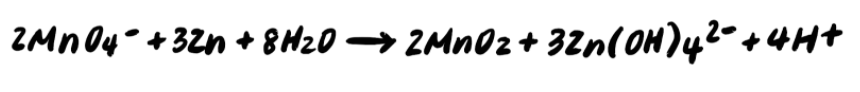
Comments